HomeResearchResearch Lines
Sustainability and Environment
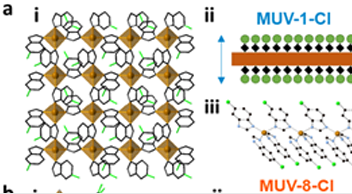
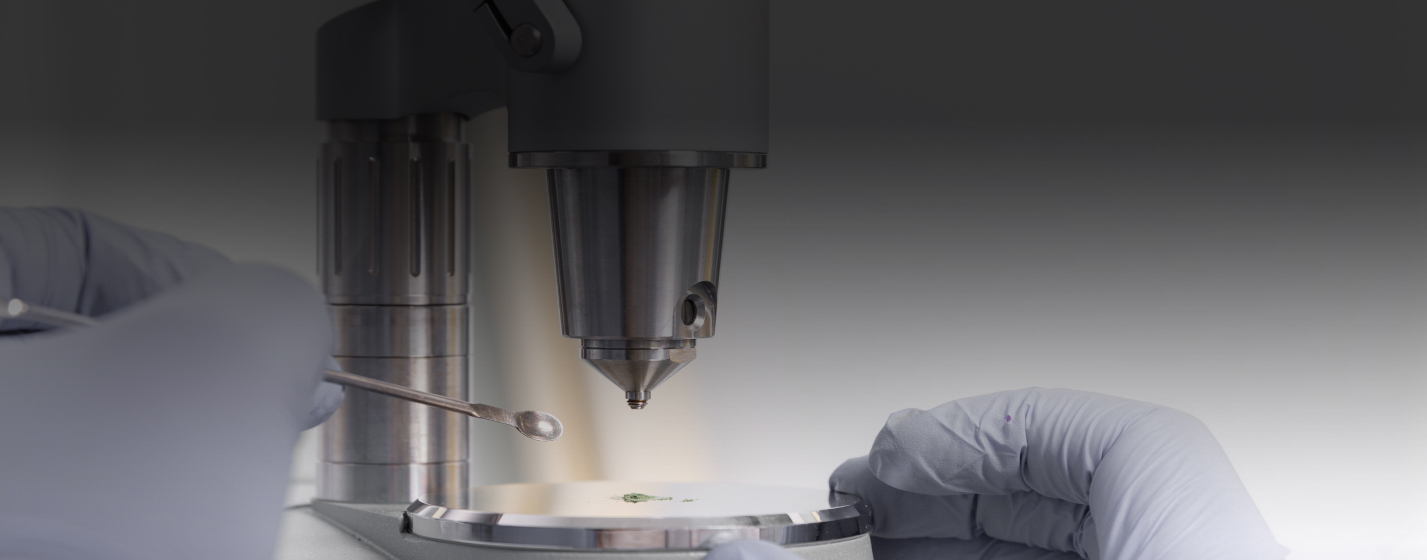
O7.1) Environmental remediation. Water is a central and threatened commodity worldwide and recycling and desalination plants are growing, while abundant sources like air humidity are still unrealistic. ICMol has started to develop nanotechnology specifically aimed at water recycling and processing, like MOFs to detoxify organics or heavy metals (ACS Appl.NanoMat. 2022, 5, 5223; WO2020109638). Exploring water sourcing from air humidity using designed porous nanomaterials and water decontamination with photoactive and magnetic nanoparticles, hybrid 2D materials, and MOFs in membranes, foams or monoliths will be our drive. O7.2) Circular Chemistry. Chemical technology is critical to industrial production, distribution, and recycling, and therefore benign alternatives have a major global impact. ICMol has enabled computational methods to optimize artificial polyesterases and boosted reactivity through enzyme confinement in porous structures (J.Am.Chem.Soc. 2023, 145, 19243). We will develop artificial enzymes to recycle more resistant plastic waste (poly-olefins, -carbamates & - amides). The confined enzymes in 3D networks to be developed will be optimized for biomass valorization (i.e. biodiesel & sugars). In addition, fine chemical production is a cornerstone of modern industry, yet based on fossil sources, and hazardous solvents and reagents that scale along the synthetic operations. ICMol has contributed with visible and NIR photochemistry using perovskite nanoparticles (J.Am.Chem.Soc. 2024, DOI:10.1021/jacs.3c14335, ACS Ener.Lett. 2023, 8, 2789) and biocompatible photoreductants to engage sustainable sources without redox reagents (i.e. J.Am.Chem.Soc. 2020, 142, 20143). We will focus on developing shorter synthetic routes using photocatalysis (radical & redox-neutral) to obtain fine-chemicals from sustainable sources, and expand research on electrochemical synthesis. O7.3) Sustainable Nanotechnology. A tool as powerful as nanotechnology has its own safety and environmental risks. ICMol responsibly deals with these and coordinates initiatives within the National Network SustainableNano. Refining the design and synthesis of nanomaterials without strategic or toxic materials can multiply the positive impact of nanotechnology. ICMol has recently developed solvent- and lead-free syntheses of perovskites (ACS Appl.Mater.Inter. 2023, 15, 32621; ACS Ener.Lett. 2023, 8, 2789), and developed syntheses of earth-abundant LDH and 2D materials (J.Am.Chem.Soc. 2023, 145, 12487; WO2023007051) and will continue developing sustainable scalable methods to obtain monodisperse luminescent nanoparticles, electrode 2D nanomaterials for sustainable Na batteries, MOFs without amide solvents, and In-free transparent electrodes.